PREPARED BY CIKGU KUNG
For MARTIN PUDU, PERMAISURI AND PANDAN INDAH students.
Saya mendoakan anda mendapat gred cemerlang dalam Kertas 1441/2 kali ini.
Final Checklist b4 taking the 1449/1/2 paper – 98 ITEMS TO REVISE
Paper 1 You must remember :
Tick ( √ ) if u understand. Sekiranya anda tidak tahu atau sudah lupa sila rujuk kembali.
- Round off a number to 2 or 3 significant figures
Be careful with the decimals like 0.006569 because 3 sf will make it as 0.00657 and not 0.01
- Express a number in standard form, A x 10 n
- express a standard form as a single number
(Reminders 2 and 3 can use calculator).
- Solve linear equations in 1 variable eg 2x – 1/3 = 5x -2
- Express a base 5 number as a number in base 8
Remember the two steps, change to base 10 first, then to base 8.
- Add and subtract numbers in base 2 using calculator.
- Changing an expanded notation to a single number
- Express a base 10 number to base 8 using the division method.
- Sum of interior angles formula in polygons
(Refer to my notes)
- Properties of rhombus, parallelogram, pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonagon and decagon.
- Sum of exterior angles in a convex polygon is 360º
- Number of sides in a regular polygon is 360º divide by 1 exterior angle
- Number of symmetries in a regular polygon is 360º divide by 1 exterior angle also
- When doing polygon questions, note every special characteristic or key words, like isosceles will mean 2 sides equal, equilateral will mean all equal sides and angles, regular will mean all sides equal….
- Know where is the angle between the tangent and a chord
- Know how to use the common tangent to solve problems on circles
- Translation must be defined by . Check which is the object before you proceed to find the image
- You must know how to find the centre of rotation and angle of rotation
- Reflection is the perpendicular line in the middle between the object and image
- Scale factor (k) is the length of the image ÷ length of the object.
- Recognize the graph of tangent, for tangent, cos and sine and the coordinates of the point of intersection between Sine and Cosine
- Pythagorean triples like 3,4 and 5 : 6, 8, and 10: etc
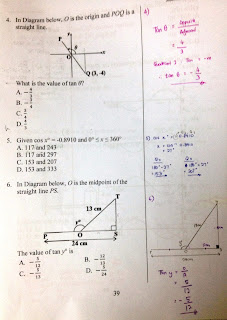
- Finding the value of tangent, cos or sine in a right angled triangle
- Where is the value of sin ө in the ordered pair of the unit circle
- Using "A S T C" to find the acute angles in the circle
- Naming the angle between a line and a plane in a cuboid
- Naming the angle between a plane and a plane in a pyramid/ prism
- Where mid points are given in the diagram, it must be used
- Angle of depression means from the top you look down
- Angle of elevation means from the bottom you look up
- Find the location of a place on the surface of the earth, ( latitude xoN/S , longitude yoE/W)
- Use ( ө x 60 ) to find the distance along the meridian/ longitude
- Use ( ө x 60 x cos latitude) to find the distance along the latitude
- Shortest distance is always along the North or South pole
- B is west of A means B is on the left
- In bearing, complete the isosceles or equilateral triangle if 3 points are given and draw up the north direction
- Use alternate angles and complete rotation to get the bearing from the point
- Bearing must be calculated starting from the North, clockwise and in 3 digits
- Be careful when the North is slanted. Draw properly.
- In algebraic formulae, the subject of the formula must always be positive value, single and preferably on the left. Skills like cross multiply, factorization and shifting must be used correctly.
- In algebraic expressions, know 4 types of factorization and expansion
- Addition and subtraction of algebraic fractions using LCM
- The 5 rules in Indices especially the bracket formula ( raising the formula)
- If you see the format of equation in Indices, make the base the same first in prime numbers
- In linear inequalities, the negative term on the right must always be changed to a positive term
- Mode is the most frequent data.
- Median is the middle value of an arranged data. Use (n+1) divide 2 to get the position of the median
- Mean is the average that is ( sum of mid points x frequency) divide by total frequency
- Calculate the sector angle in a pie chart
- Identify and draw any quadratic, reciprocal or cubic graph
- Know how to substitute a value into the given function
- In sets, list carefully the required elements before using union or intersection or prime to obtain the answer
- Unless bracket is given, solve the sets from left to right
- In the straight line, remember the 3 ways gradient is asked;
- From 2 points
- From the x and y intercepts
- From the parallel line
- From 2 points
- Remember how to find the x intercept using y=mx + c or using –y intercept / x intercept
- The equation of the straight line besides y=mx+c can also be x=b or y=c
- Finding the probability of something means the answer must be in fraction or decimal
- Know how to find probabilities in card format and in table format
- In matrices, know how to add, subtract or multiply matrices
- No inverse means ad- bc =0
- In variations, varies directly as and varies inversely as sure to come out
- Be careful with cube or cube roots in Variations
- The constant value, k, must be obtained before any further calculations
Paper 2 You must remember :
- In shading the area represented by linear functions, know the correct area to shade- above the line means greater, below the line means lesser, on the right means greater, on the left means lesser, dashed line means not inclusive of the line
- In shading the area represented by sets, number every part first before you solve the question. Remember, union means all; intersection means only the same, prime means the complement and always solve the bracket first.
- Draw a Venn diagram to show the relationship between all the sets
- In solid geometry, volumes of shapes are given but for surface area the formula given may not necessarily be correctly used for example: total surface area of hemisphere is 3π² and not 2π²
- For composite (combined) solids, make sure you need to add or minus before you proceed.
- Naming the angle between a line and a plane
The angle between the line AG and the plane ABCD is < GAC
- Naming the angle between a plane and a plane
The angle between the plane EGCA and the plane EHDA is < GEH or < CAD
- Where mid points are given in the diagram, use them
- To calculate the angle, first write out the angle, example : ABC , then use trigonometry to calculate
- In mathematical reasoning, must know meaning of statement, converse, implication, conclusion, induction and deduction
- In simultaneous equations, make one coefficient the same first before you cancel it, and then substitute to find the answer. You can use elimination or substitution method
- In straight lines, parallel lines means same gradient, know how to find the equation with a gradient and a point, how to find the coordinate of the 4th vertex in a rhombus and the x intercept of an equation
- In quadratic equations, arrange to the order of before you solve for x.
- In matrices, a matrix with no inverse means ad-bc = 0, the determinant is ad-bc and the inverse means, where i is the inverse.
- In calculating sector area, get the radius correct, the angle and then see whether you need to add or minus
- In calculating perimeter, is it whole diagram or shaded area, follow the requirement
- In probability, must know how to calculate :
- one card taken at random and two cards taken at random : the meaning of " at least one card " and "both cards "
- list the possible outcomes
- meaning of 'and' and 'or'
- one card taken at random and two cards taken at random : the meaning of " at least one card " and "both cards "
- In distance time graph, in finding the distance, refer to the y axis and for time taken refer to x axis. Average speed , length of time and total distance calculations .
- In the speed time graph, area under the graph is the distance travelled.
Must know rate of change of speed, uniform speed and distance travelled.
- Translation must be defined by .
- Reflection along the line y = - x
- Rotation of an object
- Enlargement, scale factor ½ about centre O
- In functions remember how to draw a suitable straight line !
- Practice drawing a smooth curve as this may affect your answers
- Which one is the frequency polygon? And which one is the Histogram?
- Know how to draw an Ogive
- Know Upper quartile, median, lower quartile and interquartile range
- To draw plan and elevation, view like this
- Dashed lines ( dotted lines ) are hidden lines which must be drawn
- Location of a point on the Earth is written as ( latitude , longitude )
- Diameter of the Earth means the line must pass the centre of the Earth
- Diameter of the parallel of Latitude means just opposite along the same latitude
- Latitude is either x º N or x º S. Longitude is either y º W or y º E
- Distance along of the parallel of latitude is calculated by using
θ x 60 x cos of that latitude
- Distance along the meridian is calculated by using
θ x 60
35. Speed of an airplane is distance ÷ time
GOOD LUCK. MAY THE FORCE BE WITH YOU.